Computational Science for the 21st century
Conference in honor of Professor Roland Glowinski on the occasion of his 60th
birthday
May 5-7, 1997
Tours (France)
Organization: INRIA, University of Houston and GAMNI/SMAI
Roland Glowinski's biography
Homepage of the conference CS21
ROLAND GLOWINSKI'S RESEARCH ACHIEVEMENT:
(Text written by Garret J. Etgen, University of Houston -
William E. Fitzgibbon, University of Houston -
Jacques-Louis Lions, Collège de France -
Jacques Périaux, Dassault Aviation -
Olivier Pironneau, Université Paris VI).
1. Generalities
R. Glowinski's research work can be situated at the interface between
mathematics and scientific computing, and their applications to mechanics,
physics and engineering sciences, all this including software
engineering aspects. His first investigations go back to the
mid-1960's when, as a Research Engineer at the ORTF (French
Broadcasting System), he was asked
to simulate, and then to optimize the non-linearity compensators that
were to be installed in the power transmitters for color television
which was then making its breakthrough with the general public. The
systems that he was asked to study were modelled by nonlinear
integro-differential equations. He was able to solve these equations
by using a Galerkin/finite difference method (he had just learned about these
techniques as a post-graduate numerical analysis student). Once the
simulation method had been developed and theoretically justified,
it was relatively easy to identify the system optimal parameters.
The lab tests conducted by the manufacturer, the CSF/Thomson Company,
confirmed that the parameters were indeed optimal, and this cleared the
way for the industrial production stage.
We've begun this analysis of Glowinski's research achievements with
this example because it illustrates the approach he has always
followed in his work, that is:
- Construction of a model that describes the phenomena
under investigation (most often in collaboration with the
specialists concerned).
- Identification of the model structure and mathematical properties.
- Development of numerical methods that take advantage
of the model's mathematical properties and are compatible with currently
available computing resources, as well as those that will become available
in the reasonable future.
- Wherever possible, validation of the numerical results
by experimental tests (here we have in mind complex
problems where comparisons with exact solutions
are not possible and where relevant scientific literature
often is scant).
We should add that one of Glowinski's constant concerns
has been to construct "portable" methods. By this we mean
methods that can be implemented by other scientists upon simple
reading of articles or books describing them. Although this
may seem natural, it must be said that a great many scientific
computation methods only work when implemented by their
originators since they contain "tricks" (bells and whistles)
more pertaining to Art than to Science. Specific examples,
described below, will show that this portability
objective has been attained.
2. Contributions to scientific computation methods
In the early 1970's, the major part of Glowinski's scientific activity
was concentrated on the construction of methods for the approximation and the
solution of variational inequalities in mechanics and physics. Such
inequalities, which in certain cases generalize partial differential equations,
are used to model phenomena with thresholds (plasticity, dry friction,
obstacles, etc.). They occur also in economics, finance and management. G.
Duvaut and J.L. Lions had conducted a systematic study of variational
inequalities from both the modelling and the mathematical analysis standpoints.
The problem of how to solve them numerically arose naturally out of their work.
The methods constructed by Glowinski, in collaboration with J.L. Lions and R.
Tremolieres, are essentially combinations of finite difference - or finite
element - based approximations with techniques for solving linear and non-linear
systems of equations such as penalty, duality and relaxation methods. In our
opinion, the methods, described in detail in [B.1] and updated in [B.2], remain
the most efficient methods for such type of problems and the core ideas have
not been essentially improved upon. However, in the early 1990's Glowinski, in
collaboration with Y.Kuo and G. Nasser (both engineers at NASA) improved the
way to account for the dry friction in the joints of the Space Shuttle hinged
robot arm by using the Coulomb multipliers concept, a dry friction-related
variant of Lagrange multipliers (cf. refs [149], [162], [204]).
Other notable spin-offs of Glowinski's research
investigations on variational inequalities include:
(i) A method to deal with the entropy condition in potential
compressible inviscid fluid flows.
(ii) A method to account for the incompressibility condition
in the Navier-Stokes equations modelling incompressible viscous fluid
flows.
With regard to (i), the starting point is the fact that the full potential
equations (or their variants) which model compressible perfect fluid flows may
exhibit, in the transonic or supersonic regimes, non-physical solutions, that
is, solutions containing shocks that violate the second law of thermodynamics.
To eliminate such spurious solutions, the mathematical model has to be
complemented by entropy inequalities. Glowinski was able to show that the
numerical treatment of these complemented models calls upon the variational
inequalities described in [B.1], [B.2] and [B.4] (cf. refs [B.4], [54], [56],
[58], [62], [67], [74], [99], [104], [114]). These studies led to the
computational methods used by Dassault Aviation, and to the mathematical and
numerical studies conducted by J.Necas and his school in Prague (M. Feistauer,
J.Mandel,...) on compactness by entropy for compressible flows (cf. the
publication by J.Necas: Fluid Flow: Compactness by Entropy, Masson,
Paris, 1988).
Concerning (ii), we believe that Glowinski, inspired by the
duality methods for variational inequalities, was the first to take
advantage, at the numerical level, of the fact (well-known by
continuum mechanics specialists and physicists) that for
incompressible flows the pressure may be interpreted as a Lagrange
multiplier associated with the incompressibility condition 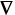 . u = 0.
This finding goes back to the late 1960's and it
led to a family of algorithms called Uzawa algorithms (since they are
related to algorithms for the search of economic equilibria investigated
by H. Uzawa). These algorithms, as applied to the solution of the
Stokes and Navier-Stokes equations, are described and analyzed in
references [B.4], [59], [82], [85], [101], [106], [110], [116],
[139], [159], [160], [171], [176]. Uzawa algorithms have motivated
the investigations of many authors and, although they were introduced
more than twenty-five years ago, they still provide efficient methods
for dealing with incompressibility and they continue to be widely used
by the scientific community.
. u = 0.
This finding goes back to the late 1960's and it
led to a family of algorithms called Uzawa algorithms (since they are
related to algorithms for the search of economic equilibria investigated
by H. Uzawa). These algorithms, as applied to the solution of the
Stokes and Navier-Stokes equations, are described and analyzed in
references [B.4], [59], [82], [85], [101], [106], [110], [116],
[139], [159], [160], [171], [176]. Uzawa algorithms have motivated
the investigations of many authors and, although they were introduced
more than twenty-five years ago, they still provide efficient methods
for dealing with incompressibility and they continue to be widely used
by the scientific community.
Still in the field of variational methods, we believe that Glowinski was the
first to realize that the augmented Lagrangian methods, introduced in
the late 1960's by Hestenes and Powell, offer considerable potential for
solving a large number of problems from mechanics and physics. These methods,
which combine the advantages of the Lagrange multiplier and penalty techniques
without having their respective drawbacks, allow one to take into account the
more or less natural decomposition principles existing in a large number
of problems. They are thus well-suited for parallel computation. Glowinksi's
intuition, advanced in the mid-1970's proved right (refs. [57], [61], followed
by [B.2], [B.3] and [B.6]).
He also showed that these methods have close links with (and are
sometimes equivalent to) the Alternating Direction (or
Operator Splitting) methods introduced in the mid-1950's by
D. Peaceman and H. Rachford, and the Fractional Step methods investigated
some years later by Y. Marchuk, N. Yanenko, R. Temam, J.L. Lions,
A. Bensoussan and others. Fractional step methods are closely
related to the Trotter theorem
in semi-group theory. Other extensions have been proposed by P.L. Lions and
B. Mercier, and by D. Gabay. Glowinski, in co-operation with M. Fortin and P. Le
Tallec, applied the augmented Lagrangian and operator splitting methods to the
solution of problems from non-Newtonian fluid mechanics (cf. [B.2], [B.3],
[B.6]), from non-linear elasticity (cf. [71], [73], [75], [77], [78], [80],
[87], [90], [95], [105], [109], [B.3], [B.6]), from electrotechnics and
telecommunications (cf. [43], [44], [B.3]), from petroleum engineering seismic
explorations (cf. [179]), and from liquid crystals and Gunzburg-Landau models
(cf. [122], [B.6], [168], [198]). New applications of these techniques are, in
fact, discovered almost every day. For example, his former collaborator
A. Marrocco successfully applied them to numerical simulation of semiconductor
phenomena and, in collaboration with A. Bensoussan, they were applied to the
solution of stochastic differential equations (ref [150], [161]).
To conclude these general comments on the methods where, in our opinion,
Glowinski has made significant contributions, we would like to mention his work
on:
- Nonlinear Least Squares Methods which allow
non-strictly variational problems to be solved by optimization techniques, possibly in
infinite dimension. These techniques have provided efficient solution methods
for non-linear problems in various fields of application such as fluid
mechanics, non-linear elasticity, etc. (cf. [39], [41], [48], [54], [55],
[56], [62], [64], [66], [67], [69], [70], [72], [81], [82], [85], [86], [90],
[94], [97], [99], [100], [102], [104], [105], [106], [107], [110], [114],
[115], [116], [118], [122], [126], [138], [147], [156], [159], [160], [176],
[B.4]).
- Domain Decomposition Methods for partial
differential equations. With parallel computing as his
driver, Glowinski has been advocating extensions of the traditional
Schwarz alternating method for more than twenty years (cf. [17]).
His methods have been applied to problems in fluid mechanics,
solid mechanics and petroleum engineering (cf. [76], [79], [81], [84], [89], [92],
[108], [112], [124], [125], [133], [135], [143], [144], [145], [146], [168],
[184], [195], [199], [200]). In particular, we
believe that Glowinski, in cooperation with M.F. Wheeler,
was the first to show how to couple domain decomposition
methods with mixed finite element approximations.
This led Wheeler and her students to the development of
computational codes of practical interest for the oil industry. It is
worth mentioning that domain decomposition methods have enjoyed
an explosive development since the late 1970's. Fundamental contributions
have been made by P. Bjorstadt, J. Bramble, F. Brezzi, T.F. Chan,
M. Drya, G.H. Golub, Y. Kuznetsov, P. Le Tallec, P.L. Lions, J. Mandel,
A. Quarteroni and O. Widlund. All these authors, including Glowinski,
have influenced each other in many ways.
- Domain Embedding/Fictitious Domain Methods for
partial differential equations. With these methods,
the solution of a problem posed in a complex-shape domain is
reduced to a problem of the same
nature in a simple-shape domain (cube, ball, etc.) which contains the
former domain and for which high-performance solution methods are
available. The price to be paid is to understand how to handle
the real boundary
"somewhere" in the method, and from this point of view, various
approaches are possible. Glowinski's principal contribution has
been to show that there is some advantage in using Lagrange
multiplier techniques. These allow one to treat the behavior
at the real boundary in the extended domain in
a relatively decentralized manner. This is of great importance
for implementation on parallel computers. This approach has led to
algorithms that are easy
to implement and to couple with operator splitting and domain
decomposition methods. Also, they are easy to use
on parallel computers for the solution of linear or non-linear
elliptic problems and for the simulation of incompressible viscous
fluid flow (cf. [184], [186], [187], [193], [195], [197], [198], [199], [200], [201]).
3. Contributions to fluid mechanics
Some of Glowinski's contributions to fluid mechanics have already been
discussed in the previous section. In this section, we
will restrict our attention to his work on:
(i) the numerical simulation of the potential flow of
compressible inviscid fluids in the transonic regime, and
(ii) the solution of the Navier-Stokes equations modeling
incompressible viscous fluid flow.
Concerning (i), the techniques he developed at the end of the
1970's, in collaboration with M.O. Bristeau, O. Pironneau and
Dassault Aviation (Company Avions Marcel Dassault at that time),
combined finite element approximations, entropy condition
treatment by penalty or upwinding methods, least square formulations,
and preconditioned conjugate gradient-type solution methods. This
work allowed Avions Marcel Dassault to score
a worldwide premiere in the early 1980's, namely the first
simulation of a three-dimensional, high Mach number,
transonic flow around a complete
aircraft (with three engine air intakes included), the Falcon 50. The
computation methods and the corresponding results are detailed in
[56], [62], [67], [68], [72], [74], [90], [99], [104], [114], [B.4].
Concerning (ii), Glowinski developed a methodology for
the numerical simulation of unsteady incompressible viscous fluid
flow where finite-element approximations and techniques for the Stokes
problem are combined with the operator splitting techniques addressed
in the previous section. In the mid 1980's, he devised a notable
time discretization method based on operator splitting (the object
being to break down incompressibility and advection). He called this
method the thêta-scheme (cf. [106], [110]). On model problems
he showed that the thêta-scheme is second
order accurate with respect to time discretization, and very stable.
Theoretical and experimental investigations conducted by R. Rannacher
and his team at the University of Heidelberg proved that this
method is second order accurate for the Navier-Stokes equations
and that it almost miraculously combines excellent properties of
stability, flexibility and easy implementation. The thêta-scheme
is systematically used at the University of Heidelberg in the FATFLOW code,
in the FASTFLO code developed at CSIRO in Australia,
at the University of Minnesota by D.D. Joseph and his team for
Newtonian and Non-Newtonian viscous fluid flow simulations; and
by A. Sameh and his team, now at Purdue University.
The thêta-scheme is also used by P. Saramito at the University
of Grenoble for visco-elasticity phenomena simulations.
To conclude this discussion of Glowinski's contributions to fluid
mechanics, we would like to mention his investigations
with P. Ciarlet and O. Pironneau in which they elucidated
(completely, in our opinion) the problem - considered
tricky - of adjusting the vorticity boundary conditions in the stream
function-vorticity formulation of the Navier-Stokes equations. This
led to a bi-harmonic solver based on the finite-element method which
is efficient and well-suited to complex-shape domains (cf. [6], [7],
[21], [30], [36], [37], [45], [47], [53], [60], [102], [156], [167]).
4. Contributions to solid and structure mechanics
Concerning R. Glowinski's contributions to solid and structural
mechanics, we shall mention his investigations on:
(i) the numerical simulation of the static and dynamic
behavior of the flexible pipelines used in the petroleum industry
for offshore operations, and
(ii) incompressible and slightly compressible non-linear
elasticity.
The investigations related to (i) go back to the late 1970's
and are described in [71], [75], [B.3], [B.6]. The oil industry was
looking for a methodology able to simulate the static and dynamic
behavior of flexible pipelines used in offshore operations. Such pipelines
usually exhibit very large displacements and the classical
finite element methods used at that time were not adequate. Glowinski
was consulted on these problems and he quickly realized that the augmented
Lagrangian methods (developed for other problems; see Section 2) when
combined with convenient finite-element approximations, was ideally suited
to the solution of these nonlinear elastic problems. This
led to a simulator and Glowinski was quite pleased to learn,
recently, that this simulator is still used by some very large
oil industry companies more than fifteen years
after its creation.
Regarding these flexible pipelines, we note that the pipe consists
of a multi-layer material exhibiting internal dry friction
phenomena. The methods developed by Glowinski for the simulation
of dry friction phenomena have been used by Institut Français du
Pétrole (IFP) for the simulation of pipeline oscillations, and the
correlation with lab experiments (damping time constants,
oscillation frequencies and amplitudes) proved excellent.
The contributions related to (ii) come from investigating
materials such as rubber, which is obviously elastic, practically
incompressible, and able to handle very large displacements and
deformations when subjected to various types of loads. Here again,
taking the tensor 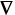 u (where u is the displacement) as the
main unknown, the elasto-static problems for this type of material
are ideally suited to augmented Lagrangian solution methods in both
two and three-dimensions. This led to the methods
and results discussed in [B.3], [B.6] and [73], [75], [77], [78],
[80], [87], [95], [105], [109], which were obtained in cooperation with his
former student P. Le Tallec, currently Professor of Mechanics at Ecole
Polytechnique.
u (where u is the displacement) as the
main unknown, the elasto-static problems for this type of material
are ideally suited to augmented Lagrangian solution methods in both
two and three-dimensions. This led to the methods
and results discussed in [B.3], [B.6] and [73], [75], [77], [78],
[80], [87], [95], [105], [109], which were obtained in cooperation with his
former student P. Le Tallec, currently Professor of Mechanics at Ecole
Polytechnique.
We shall conclude this section by mentioning that:
- Glowinski's augmented Lagrangian methods have been extended to
other non-linear elasticity problems by R.L. Taylor (University of California -
Berkeley) and the late J. Simo (at Stanford University).
- Glowinski's intuition concerning the favorable parallelization
properties of augmented Lagrangian methods has been verified
in Germany by M. Shafer (on a DAP machine) who solved
problems from nonlinear incompressible elasticity using the
techniques mentioned above.
5. Contributions to the numerical solution of control problems for distributed systems
The term distributed systems classically refers to all systems
whose behavior can be modelled by partial differential equations. Although
control problems and their numerical solutions have always been of great
interest to Glowinski, it was only in 1986, following J.L. Lions'
investigations on controllability using the Hilbert Uniqueness
method (HUM), that he began to dedicate a considerable part
of his research activities to this topic, in collaboration with
J.L. Lions. This led to:
(i) The development of approximation and iterative
solution methods operating directly on the initial (primal) problem
or, in the sense of HUM, on a dual problem. This allowed the solution
of optimal control problems and exact or approximate controllability
problems for the wave equation, the heat equation, the Euler-Bernoulli
vibrating beam equation and the Navier-Stokes equations (cf. [138],
[142], [143], [148], [153], [163], [166], [171], [189], [190], [194], [196],
[202], [206]). In the case of the wave equation, implementation of
the HUM method raises delicate approximation problems since
discretization by the usual methods of a well-posed problem may lead to
finite-dimensional problems that are very poorly conditioned and to
solutions which contain spurious high frequencies and high
amplitude oscillations. Glowinski and his collaborators developed
two types of methods to overcome these difficulties; one based on a
regularization method à la Tychonoff (refs. [138],
[142]), and another based on a judicious choice of the approximation
spaces where unwanted high-frequency components are eliminated by
construction (cf. [148], [171], [202]). The latter draws its
inspiration from approximation methods for the Stokes problem
in fluid mechanics with which (cf. [171]) the problem of exact
controllability shows a certain number of
formal analogies. Glowinski was awarded the Seymour Cray Prize in
1988 for his contributions on Exact Controllability of
the Wave Equation. In 1995, his Ph.D. student, M. Berggren,
received the "SIAM Prize for Best Student Article" (SIAM:
Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics) for his work on the control
of the Navier-Stokes equations.
(ii) The development of methods, based on control and
exact controllability, which speed up the convergence of some
dynamical systems to limit cycles (when such cycles exist). These
methods, introduced in [115], have led to very efficient algorithms
for solving scattering problems at moderately large wave numbers, i.e.
in those situations where the wave length is small compared to the
characteristic length of the obstacle but not small enough to allow
the methods of geometrical optics. These algorithms can be seen as
impulse control methods where one periodically perturbs the evolution
of the system in order to reach, as fast as possible, a limit cycle.
For these investigations (described in [175], [180], [181], [182],
[189], [194], [202]) and other contributions, Glowinski's collaborators and
former Ph.D. students, M.O. Bristeau and J. Periaux, received the "1993
Science and Defense Prize" awarded by the French Department of
Defense.
The methods indicated above have good parallelization properties,
as shown in [182].
6. Other contributions
The essence of R. Glowinski's scientific activity has been
summarized in Sections 2 through 5, but there are additional noteworthy
contributions which we should also mention. For example, he undertook a number
of studies on gas lubrication problems in collaboration with
SAGEM, on shape optimization in fluid and structural mechanics
(refs. [10], [20], [28], [29], [34], [35], [51], [68], [193], [201]),
on electron transport in the Earth's magnetosphere (refs. [103],
[B.5]), on stellar motion (ref. [96]) in collaboration with E.
Schatzman, and on the Boltzmann Equation modelling exotic
semiconductor materials such as gallium arsenide (ref. [152]). These last
investigations, conducted jointly with J.F. Palmier of CNET and
J.F. Bourgat of INRIA in the
mid-1980's, led to a simulation program which is still in use. We
conclude by mentioning Glowinski's investigations on the
wavelets solution of partial differential equations (ref. [151]).
7. Comments on R. Glowinski's collaborators
Throughout his career, R. Glowinski was fortunate
to enjoy collaborations with scientists of outstanding quality.
The names of most of them are quoted in the two reference lists.
Some among these collaborators were his Ph.D. students who were later
recognized for their own individual achievements:
- M.O. Bristeau and J. Periaux - awarded the Science and
Defense Prize from the French Department of Defense.
- P. Le Tallec - awarded the CISI Prize and the Blaise
Pascal Prize of the French Academy of Sciences.
- B. Stoufflet - awarded the IBM Prize and the Blaise Pascal
Prize of the French Academy of Sciences.
- A. Dervieux - awarded the IBM Prize and the Seymour Cray
Prize.
- M. Berggren - awarded in 1995 the SIAM Prize for the best
Ph.D. related article in Applied Mathematics.
8. Thesis supervision
Roland Glowinski has supervised the "Thèses d'État" of Alain
Dervieux, Patrick Le Tallec, Bertrand Mercier and Vittoriano Ruas at
Université Pierre et Marie Curie (Paris VI), the Ph.D. Theses of Alfredo
Carrizosa, Craig Carthel, Luis de Loura, George Nasser, Guohua Ruan, Francisco
Sanchez, Jurgen Singer and Vassilis Zafiris at the University of Houston and of
Martin Berggren and Anthony Kearsley at Rice University.
He has also supervised more than fifty "Thèses d'Université,
Thèses du Nouveau Régime" all at the Université
Pierre et Marie Curie, and ten Master theses at the University of Houston.
9. Final remarks
In conclusion we would like to add the following remarks:
- R. Glowinski took advantage of his long term stays in the United
States to strengthen the ties of scientific and technical
collaboration between France and the U.S.A. This was achieved either
in the formal context of the CNRS-NSF cooperation agreement under
which visits of scientists from the two countries were
encouraged, or through the organization of conferences, lectures and
workshops, notably on the topics of domain decomposition methods for
partial differential equations and mathematical
modelling and numerical simulation of supersonic and hypersonic
flows. These efforts, we believe, have been highly beneficial to
international scientific cooperation.
- If we were to situate R. Glowinski from a scientific standpoint,
we would say that he occupies a position at the intersection of
mathematics and its applications to mechanics and physics,
scientific computing, computer science, and engineering.
The umbrella encompassing these fields is now known as Computational Science.
BIBLIOGRAPHY:
BOOKS
B1. R. GLOWINSKI, J. L. LIONS, R. TREMOLIERES, Analyse
Numérique des Inéquations Variationnelles, Dunod, Paris,
1976.
B2. R. GLOWINSKI, J. L. LIONS, R. TREMOLIERES, Numerical Analysis of
Variational Inequalities, North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1981.
B3. M. FORTIN, R. GLOWINSKI, Lagrangiens Augmentés, Dunod,
Paris, 1982.
B4. R. GLOWINSKI, Numerical Methods for Nonlinear Variational Problems,
Springer-Verlag, New York, 1984.
B5. M. BLANC, D. FONTAINE, R. GLOWINSKI, L. REINHART, Simulation of
Electron Transport in the Earth Magnetosphere, Gordon and Breach, New York, 1987.
B6. R. GLOWINSKI, P. LE TALLEC, Augmented Lagrangians and Operator
Splitting Methods in Nonlinear Mechanics, SIAM, Philadelphia, 1989.
ARTICLES
1. R. GLOWINSKI, Résolution numérique d'un
problème non-classique de calcul des variations, in Symposium on
Optimization, Lecture Notes in Mathematics, Vol. 132,
Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1970, pp. 108-129.
2. R. GLOWINSKI, Etude et approximation de quelques problèmes
intégraux et intégro-différentiels, Thèse
d'Etat, Université de Paris VI, 1970.
3. R. GLOWINSKI, Méthodes numériques pour l'écoulement
stationnaire d'un fluide rigide visco-plastique incompressible, in
Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Numerical Methods in
Fluid Dynamics, M. Holt ed., Lecture Notes in Physics, Vol. 8,
Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1971, pp. 385-394.
4. R. GLOWINSKI, La méthode de relaxation, application à la
minimisation des fonctionnelles convexes, Rendi Conti di Matematica,
Vol. 14, Rome, 1971.
5. J. CEA, R. GLOWINSKI, J.C. NEDELEC, Minimisation de fonctionnelles non
différentiables, in Conference on Applications of Numerical
Analysis, Morris ed., Lecture Notes in Mathematics, Vol. 228,
Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1971, pp. 19-38.
6. R. GLOWINSKI, Sur une méthode d'approximation externe, par
éléments finis d'ordre deux, du problème de Dirichlet pour
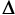 2 et méthode itérative de résolution du
problème approché (I), C. R. Acad. Sc., Paris, T. 275
A, (1972), pp. 201-204.
2 et méthode itérative de résolution du
problème approché (I), C. R. Acad. Sc., Paris, T. 275
A, (1972), pp. 201-204.
7. R. GLOWINSKI, Sur une méthode d'approximation externe, par
éléments finis d'ordre deux, du problème de Dirichlet pour
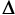 2 et méthode iterative de résolution du
problème approché (II), C. R. Acad. Sc., Paris, T. 275
A, (1972), pp.333-335.
2 et méthode iterative de résolution du
problème approché (II), C. R. Acad. Sc., Paris, T. 275
A, (1972), pp.333-335.
8. J. CEA, R. GLOWINSKI, Méthodes numériques pour
l'écoulement laminaire d'un fluide rigide, visco-plastique,
incompressible, International Journal of Computer Mathematics, Sec. B,
Vol. 3, (1972), pp. 225-255.
9. D. BEGIS, R. GLOWINSKI, Dual numerical techniques, application to an
optimal control problem, in Techniques of Optimization, A.V.
Balakrishnan ed., Academic Press, New York, 1972, pp. 159-174.
10. D. BEGIS, R. GLOWINSKI, Some numerical problems in optimal control of
distributed systems related to variational inequalities and optimal domain
problems, in Proceedings of the 1972 IEEE Conference on Decision and
Control, IEEE publication, 1972, pp. 366-369.
11. R. GLOWINSKI, Approximation numérique des solutions
périodiques d'une équation intégro-différentielle, Journal of Math.
Analysis and Applications, Vol. 41, No. 1, (1973), pp. 67-96.
12. R. GLOWINSKI, Approximations externes par éléments finis
d'ordre un et deux du problèm de Dirichlet pour l'opérateur
biharmonique. Méthode itérative de résolution des
problèmes approchés, in Topics in Numerical Analysis, J.H.
Miller ed., Academic Press, London, 1973, pp. 123-171.
13. R. GLOWINSKI, Sur la minimisation, par surrelaxation avec projection, de
fonctionnelles quadratiques dans les espaces de Hilbert, C. R. Acad.
Sc., Paris, T. 276A, (1973), pp. 1421-1423.
14. R. GLOWINSKI, Méthodes itératives duales pour la
minimisation de fonctionnelles convexes, in Constructive Aspects of
Functional Analysis, Edizioni Cremonesa, Rome, 1973, pp. 263-292.
15. J. CEA, R. GLOWINSKI, Sur des méthodes de minimisation par
relaxation, Revue Francaise d'Automatique, Informatique, Recherche
Operationnelle, Serie Rouge, Dec. 1973, R-3, pp. 5-32.
16. R. GLOWINSKI, H. LANCHON, Torsion elasto-plastique d'une barre de section
multi-connexe, Journal de Mécanique, Vol. 1, Mars 1973,
pp. 151-171.
17. A. BENSOUSSAN, R. GLOWINSKI, J. L. LIONS, Méthodes de
décomposition appliquées au contrôle optimal de
systèmes distribués, in Proceedings of the Fifth IFIP
Conference on Optimization Techniques, Part 2, Lecture Notes in Computer
Sciences, Vol. 3, Springer, Berlin, 1973, pp. 141-153.
18. R. GLOWINSKI, Sur l'écoulement d'un fluide de Bingham dans une
conduite cylindrique, Journal de Mécanique, Vol. 13, No.
4, (1974), pp. 601-621.
19. J. CEA, R. GLOWINSKI, J. C. NEDELEC, Application des méthodes
d'optimisation, de différences et d'éléments finis
à l'analyse numérique de la torsion elasto-plastique d'une barre
cylindrique, in Approximation et Méthodes Iteratives de
résolution d'Inéquations Variationnelles et de Problèmes
non Linéaires, Cahier de l'IRIA No. 12, Mai 1974, pp. 7-138.
20. D. BEGIS, R. GLOWINSKI, Application de la méthode des
éléments finis à la résolution d'un problème
de domaine optimal, in Computing Methods in Applied Sciences and
Engineering, R. Glowinski, J. L. Lions eds., Lecture Notes in Computer
Sciences, Vol. 11, Springer Verlag, Berlin, 1974, pp. 403-434.
21. P. G. CIARLET, R. GLOWINSKI, Sur la résolution numérique du
problème de Dirichlet pour l'opérateur biharmonique, C. R.
Adad. Sc., Paris, T. 279 A, (1974), pp. 239-241.
22. M. O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, Finite Element Analysis of the unsteady flow
of a visco-plastic fluid in a cylindrical pipe, in Finite Element Methods in
Flow Problems, J. T. Oden, O.C. Zienkiewicz, R. H. Gallagher, C. Taylor
eds., University of Alabama Press, Huntsville, 1974, pp. 471-488.
23. R. GLOWINSKI, A. MARROCCO, Etude numérique du champ
magnétique dans un alternateur tetrapolaire par la méthode des
éléments finis, in Computing Methods in Applied Sciences and
Engineering, R. Glowinski et J. L. Lions eds., Lecture Notes in Computer
Sciences, Vol. 10, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1974, pp. 292-316.
24. R. GLOWINSKI, A. MARROCCO, Analyse Numérique du Champ
Magnétique d'un Alternateur par Eléments Finis et Surrelaxation
Ponctuelle non linéaire, Computer Methods in Applied Mech. and
Engineering, Vol. 13, No. 1, (1974), pp. 55-85.
25. R. GLOWINSKI, A. MARROCCO , Sur l'approximation par éléments
finis d'ordre 1 et la résolution par pénalisation-dualité,
d'une classe de problèmes de Dirichlet non linéaires, C. R.
Acad. Sc., Paris, T. 278A, (1974), pp. 1649-1652.
26. R. GLOWINSKI, A. MARROCCO, On the solution of a class of non-linear
Dirichlet problems by a penalty-duality method and finite element of order one,
in Optimization Techniques IFIP Technical Conference, G.I. Marchouk ed.,
Lecture Notes in Computer Sciences, Vol. 27, Springer-Verlag, Berlin,
1974, pp. 327-333.
27. R. GLOWINSKI, Analyse Numérique d'Inéquations
Variationnelles d'Ordre 4, Rapport 75002, Laboratoire d'Analyse
Numérique, L.A. 189, Universite Pierre et Marie Curie, 1975.
28. D. BEGIS, R. GLOWINSKI, Application de la méthode des
éléments finis à l'approximation d'un problème de
domaine optimal. Méthode de résolution des problèmes
approchés, Applied Math. and Optimization, Vol. 2, 2,
(1975), pp. 130-169.
29. R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, On the numerical computation of the
minimum-drag profile in laminar flow, J. Fluid Mech., Vol. 72,
Part 2, (1975), pp. 385-389.
30. P. G. CIARLET, R. GLOWINSKI, Dual iterative techniques for solving a
finite element approximation of the biharmonic equation, Comp. Math. Applied
Mech. Eng., 5, (1975), pp. 277-295.
31. R. GLOWINSKI, A. MARROCCO, Sur l'approximation par éléments
finis et la résolution par pénalisation-dualité d'une
classe de problèmes de Dirichlet non linéaires, Revue
Française d'Automatique, Informatique, Recherche Operationnelle,
Serie Rouge (Analyse Numérique), R-2, (1975), pp. 41-76.
32. R. GLOWINSKI, Sur l'approximation d'une inéquation variationnelle
de type Bingham, Revue Française d'Automatique, Informatique,
Recherche Operationnelle, Serie Rouge (Analyse Numérique),(1976),
pp.13-30.
33. R. GLOWINSKI, Introduction to the Approximation of Elliptic Variational
Inequalities, Rapport 76006, Laboratoire d'Analyse Numérique, L.A.
189, Universite Pierre et Marie Curie, 1976.
34. J. M. BOISSERIE, R. GLOWINSKI, Optimisation de la loi d'épaisseur
pour une coque mince de révolution, in Computing Methods in Applied
Sciences and Engineering, R. Glowinski, J. L. Lions eds., Lecture Notes in
Economics and Math. Systems, Vol. 134, Springer, Berlin, 1976, pp.
258-275.
35. R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, Toward the computation of minimum drag
profiles in viscous laminar flow, Applied Mathematical Modelling,
Vol. 1, (1976), pp. 58-66.
36. R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, Sur la résolution numérique du
problème de Dirichlet pour l'opérateur biharmonique par une
méthode "quasi-directe", C. R. Adad. Sc. Paris, T. 282A,
(1976), pp. 223-226.
37. R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, Sur la résolution numérique du
problème de Dirichlet pour l'opérateur biharmonique par une
méthode de gradient conjugué, Applications, C. R. Adad.
Sc. Paris, T. 282A, (1976), pp. 1315-1318.
38. R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, Sur la résolution par une
méthode quasi-directe et par diverses méthodes itératives
d'une approximation par éléments finis mixtes du problème
de Dirichlet pour 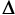 2, Rapport 76010, Laboratoire d'Analyse
Numérique, L.A. 189, Universite Pierre et Marie Curie, 1976.
2, Rapport 76010, Laboratoire d'Analyse
Numérique, L.A. 189, Universite Pierre et Marie Curie, 1976.
39. R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, Calculs d'écoulements
transsoniques par des méthodes d'elements finis et de contrôle
optimal, in Computing Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering, R.
Glowinski, J.L. Lions eds., Lecture Notes in Economics and Math. Systems,
Vol. 134, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1976, pp. 276-296.
40. R. GLOWINSKI, A. MARROCCO, Finite element approximation and iterative
methods of solution for 2-D non-linear magnetostatic problems, Proceedings
of the 1st COMPUMAG Conference, Oxford, April 1976, Rutherford Laboratory
publication, pp. 112-125.
41. R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, O. PIRONNEAU, Use of Optimal Control Theory for
the numerical simulation of transonic flows by the method of finite elements,
in Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Numerical Methods in
Fluid Dynamics, A.I. Van de Vooren, P. J. Zandbergen eds., Lecture Notes in
Physics, Vol. 59, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1976, pp. 205-211.
42. R. GLOWINSKI, Sur la résolution du problème de Stokes dans
un domaine multiplement connexe par une méthode de fonction de courant,
C. R. Acad. Sc., Paris, T. 284A, (1977), pp. 675-678.
43. M. FELDMAN, R. GLOWINSKI, A. GUERARD, Synthèse par Optimalisation
des filtres à ondes élastiques de surface, Annales des
Télécommunications, T. 32, 1-2, Janvier-Fevrier,
(1977), pp. 37-48.
44. R. GLOWINSKI, A. MARROCCO, Numerical solution of two dimensional
magneto-static problems by augmented Lagrangian methods, Comp. Methods Appl.
Mech. Eng., Vol. 12, (1977), 1, pp. 33-46.
45. R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, Solving a mixed finite element approximation
of the Dirichlet problem for the biharmonic operator by a "quasi-direct" method
and various iterative methods, in Mathematical Aspects of Finite
Elements, I. Galligani, E. Magenes, eds., Lecture Notes in Math., Vol. 606,
Springer-Verlag, 1977, pp. 167-193.
46. R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, Numerical methods for the first biharmonic
equation and for the two-dimensional Stokes problem, Stanford Report,
STAN-CS-77-615, Comp. Science Dept., May 1977.
47. R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, Sur une méthode quasi-directe pour
l'opérateur biharmonique et ses applications à la
résolution des équations de Navier-Stokes, Annales des
Sciences Math. du Quebec, Vol. 1, (1977), 2, pp. 231-245.
48. M. O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, Numerical solution of the
transonic equation by finite element methods via Optimal Control, in Control
Theory of Systems Governed by Partial Differential Equations, A. K. Aziz,
J. W. Wingate, M.J. Balas , eds., Academic Press, 1977, pp. 265-278.
49. R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, Approximation par éléments finis
mixtes du problème de Stokes en formulation vitesse-pression.
Convergence des solutions approchés, C. R. Acad. Sc., Paris,
T. 286A, (1978), pp. 181-183.
50. R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, Approximation par éléments finis
mixtes du problème de Stokes en formulation vitesse-pression.
Résolution des problèmes approchés. C. R. Acad.
Sc., Paris, T. 286A, (1978), pp. 225-228.
51. J. M. BOISSERIE, R. GLOWINSKI, Optimization of the thickness law for thin
axisymetric shells, Computers and Structures, Vol. 8, (1978), pp.
331-343.
52. R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, Sur la résolution via une approximation
par éléments finis mixtes du problème de Dirichlet pour
l'opérateur biharmonique par une méthode "quasi-directe" et
diverses méthodes itératives, in Etude Numérique des
Grands Systèmes, J. L. Lions, G. I. Marchouk eds., Dunod-Bordas,
Paris, 1978, pp. 151-181.
53. R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, Numerical solution for the two-dimensional
Stokes problem through the stream-function vorticity formulation, in
Functional Analysis and Numerical Analysis, Japan-France Seminar, Tokyo
and Kyoto, 1976, H. Fujita, ed., Japan Society for the Promotion of Science,
1978, pp. 99-142.
54. R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, On the computation of transonic flows, in
Functional Analysis and Numerical Analysis, Japan-France Seminar, Tokyo
and Kyoto, 1976, H. Fujita, ed., Japan Society for the Promotion of Science,
1978, pp. 143-173.
55. R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, O. PIRONNEAU, Transonic flow simulation by the
Finite Element Method via Optimal Control, Chapter 11 of Finite Elements in
Fluids, Vol. 3, R. H. Gallagher, O.C. Zienkiewicz, J.T. Oden, M.
Morandi Cecchi, C. Taylor, eds., J. Wiley & Sons, London, 1978.
56. M. O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, P. PERRIER, O. PIRONNEAU, G.
POIRIER, Application of Optimal Control and Finite Element Methods to the
calculation of Transonic Flows and Incompressible Viscous Flows, in
Numerical Methods in Applied Fluid Dynamics, B.Hunt, ed., Academic
Press, London, 1980, pp. 203-320.
57. T.F. CHAN, R. GLOWINSKI, Finite Element Approximation and Iterative
Solution of a Class of Mildly Non-Linear Elliptic Equations, Stanford
Report, STAN-CS-78-674, Comp. Science Dpt., Nov. 1978.
58. R. GLOWINSKI, Finite Elements and Variational Inequalities, Chapter 12 of
The Mathematics of Finite Elements and Applications, III, J.R. Whiteman
ed., Acad. Press, London, 1979, pp. 135-171.
59. R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, On Numerical Methods for the Stokes Problem,
Chapter 13 of Energy Methods in Finite Element Analysis, R. Glowinski,
E.Y. Rodin, O.C. Zienkiewicz eds., J. Wiley & Sons, 1979, pp. 243-264.
60. R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, Numerical methods for the first biharmonic
equation and for the two-dimensional Stokes problem, SIAM Review,
Vol. 17, (1979), 2, pp. 167-212.
61. T. F. CHAN, R. GLOWINSKI, Numerical Methods for a class of mildly
nonlinear elliptic equations, Atas do Decimo Primeiro Coloquio Brasileiro de
Matematicas, Vol. I, C.N.D.C.T./IMPA, Rio de Janeiro, (1978), pp.
279-318.
62. M.O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, P. PERRIER, O. PIRONNEAU, On the
numerical solution of nonlinear problems in fluid dynamics by least squares and
finite element methods. (I) Least square formulations and conjugate gradient
solution of the continuous problems, Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng.,
17/18, (1979), pp. 619-657.
63. R. GLOWINSKI, On grid optimization for boundary value problems,
Stanford Report STAN-CS-79-720, Feb. 1979, Comp. Science Dept., Stanford
University.
64. M.O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, B. MANTEL, J. PERIAUX, P. PERRIER, O.
PIRONNEAU, A finite element approximation of Navier-Stokes equations for
incompressible viscous fluids. Iterative methods of solution, in
Approximation Methods for Navier-Stokes Problems, R. Rautman ed.,
Lecture Notes in Mathematics, Vol. 771, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1979,
pp. 78-128.
65. R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, On a mixed finite element approximation of the
Stokes problem (I), Convergence of the approximate solutions, Numerische
Mathematik, 33, (1979), pp. 397-424.
66. R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, O. PIRONNEAU, An efficient preconditioning
scheme for iterative numerical solution of partial differential equations,
Applied Math. Modelling, Vol. 4, (1980),pp. 187-192.
67. M.O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, P. PERRIER, G. POIRIER, Transonic
flow simulation by finite element and least square methods, in Finite
Elements in Fluids, Vol. 4, R. H. Gallagher, D. H. Norris, J. T.
Oden, O.C. Zienkiewicz eds., John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, 1982, pp.
453-482.
68. F. ANGRAND, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, P. PERRIER, G. POIRIER, O.
PIRONNEAU, Optimum Design for Potential Flows, in Proceedings of the Third
International Conference on Finite Elements in Flow Problems, Banff,
Alberta, Canada, 10-13 June 1980, Vol. 1, D.H. Norrie ed., pp.
400-412.
69. R. GLOWINSKI, B. MANTEL, J. PERIAUX, P. PERRIER, O. PIRONNEAU, On an
efficient new preconditioned conjugate gradient method. Application to the in
core solution of the Navier-Stokes equations, in Finite Elements in
Fluids, R.H. Gallagher, D. H. Norrie, J.T. Oden, O.C. Zienkiewicz eds.,
John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, 1982, pp. 365-401
70. R. GLOWINSKI, B. MANTEL, J. PERIAUX, O. PIRONNEAU, A finite element
approximation of Navier-Stokes equations for incompressible viscous fluids.
Functional least-square methods of solution, in Computer Methods in
Fluids, K. Morgan, C. Taylor, C.A. Brebbia, eds., Pentech Press, London,
1980.
71. J. F. BOURGAT, J.M. DUMAY, R. GLOWINSKI, Large displacements calculations
of flexible pipelines by finite element and nonlinear programming methods, SIAM
J. Sc. Stat. Comp., 1, (1980), pp. 34-81.
72. R. GLOWINSKI, B. MANTEL, J. PERIAUX, O. PIRONNEAU, G. POIRIER, An
efficient preconditioned conjugate gradient method applied to nonlinear
problems in fluid dynamics via least squares formulation, in Computing
Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering, R. Glowinski, J.L. Lions eds.,
North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1980, pp. 445-487.
73. R. GLOWINSKI, P. LE TALLEC, Une méthode numérique en
élasticité non linéaire incompressible, C.R.A.S.
Paris, T.290B, (1980), pp. 23-26.
74. R. GLOWINSKI, A Variational Inequality Approach to Transonic Flow
Simulation via Finite Elements and Nonlinear Least Squares, in Free Boundary
Problems, Vol. II, Instituto Nazionale di Alta Mathematica,
Francesco Severi, Roma, 1980, pp. 299-320.
75. J.F. BOURGAT, R. GLOWINSKI, P. LE TALLEC, Decomposition of Variational
Problems. Applications in Finite Elasticity, in Partial Differential
Equations in Engineering and Applied Sciences, R.L. Sternberg ed., Marcel
Dekker, New York, 1980, pp. 445-480.
76. Q. V. DINH, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, Résolution numérique
des équations de Navier-Stokes par des méthodes de
décomposition de domaines, in Méthodes numériques dans
les Sciences de l'Ingénieur, GAMNI 2, Vol. 1, E. Absi, R.
Glowinski, P. Lascaux, H. Veysseyre eds., Dunod, Paris, 1980, pp. 383-404.
77. R. GLOWINSKI, P. LE TALLEC , V. RUAS, Approximate solution of nonlinear
problems in incompressible finite elasticity, in Nonlinear Finite Element
Analysis in Structural Mechanics, W. Wunderlich, E. Stein, K. J. Bathe
eds., Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1981, pp. 666-695.
78. R. GLOWINSKI, P. LE TALLEC, Numerical solution of problems in
incompressible finite elasticity by augmented lagrangian methods. (I)
Two-dimensional and axisymmetric problems, SIAM J. of Applied Math.,
42, (1982), pp. 400-425.
79. Q.V. DINH, R. GLOWINSKI, B. MANTEL, J. PERIAUX, P. PERRIER, Subdomain
solution of nonlinear problems in fluid dynamics on parallel processors, in
Computing Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering V, R. Glowinski,
J. L. Lions eds., North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1982, pp. 123-164.
80. R. GLOWINSKI, P. LE TALLEC, Elasticité Non Linéaire:
Formulation Mixte et Méthode Numérique Associée, in
Computing Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering, V, R. GLOWINSKI,
J. L. Lions eds., North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1982, pp. 281-297.
81. Q.V. DINH, R. GLOWINSKI, B. MANTEL, J. PERIAUX, On the numerical
simulation of incompressible viscous fluids modelled by the Navier-Stokes
equations. Related domain decomposition methods, in Comptes-Rendus du
Symposium sur la Modélisation Fine des Ecoulements, Vol. 1,
J. P. Benque ed., Presses de l'Ecole Nationale des Ponts et Chaussees, 1982,
pp. 275-317.
82. R. GLOWINSKI, B. MANTEL, J. PERIAUX, Numerical solution of the time
dependent Navier-Stokes equations for incompressible viscous fluids by finite
element and alternating direction methods, in Numerical Methods in
Aeronautical Fluid Dynamics, P. L. Roe ed., Acad. Press, London, 1982, pp.
309-336.
83. Q.V. DINH, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, Domain Decomposition Methods for
Nonlinear Problems in Fluid Dynamics, Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng.,
40, (1983), pp. 27-109.
84. Q.V. DINH, R. GLOWINSKI, B. MANTEL, J. PERIAUX, Approximate Solution of
the Navier-Stokes Equations for Incompressible Viscous Fluids. Related Domain
Decomposition Methods, in Numerical Methods, Proceedings, Caracas, 1982,
V. Pereyra, A. Reineza eds., Lecture Notes in Math; Vol. 1005,
Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1983, pp. 46-86.
85. R. GLOWINSKI, Numerical methods for the time dependent Navier-Stokes
equations for incompressible viscous fluids, in Proceedings of the
China-France Symposium on Finite Element Methods, Feng Kang et J. L. Lions
eds., Gordon and Breach, New York, 1983, pp. 265-292.
86. R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, O. PIRONNEAU, An efficient preconditioned
conjugate gradient method. Application to the solution of nonlinear problems in
Fluid Dynamics, in Preconditioning Methods. Theory and Applications, D.
J. Evans ed., Gordon and Breach, 1983, pp. 463-508.
87. R. GLOWINSKI, P. LE TALLEC, Finite Elements in Nonlinear Incompressible
Elasticity, Chapter 2 of Finite Elements, Special Problems in Solid
Mechanics, Vol. V, J. T. Oden, G. F. Carey, eds., Prentice Hall,
N.J., 1984, pp. 67-93.
88. H. BERESTYCKI, E. FERNANDEZ-CARA, R. GLOWINSKI, A Numerical study of some
questions in vortex ring theory, RAIRO, Analyse Numérique,
18, (1984), 1, pp. 7-85.
89. Q.V. DINH, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, Domain decomposition for elliptic
problems, in Finite Elements in Fluids, Vol. V, R. H. Gallagher,
J. T. Oden, O. C. Zienkiewicz, T. Kawai, M. Kawahara eds., Wiley, Chichester,
1984, pp. 45-106.
90. R. GLOWINSKI, Numerical Simulation for Some Applied Problems Originating
from Continuum Mechanics, in Trends and Applications of Pure Mathematics to
Mechanics, P. G. Ciarlet and M. Roseau eds., Lecture Notes in Physics, Vol.
195, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1984, pp. 96-145.
91. R. GLOWINSKI, L. D. MARINI, M. VIDRASCU, Finite-element Approximations and
Iterative Solutions of a Fourth-Order Elliptic Variational Inequality, IMA
Journal of Numerical Analysis, 4, (1984), pp. 127-167.
92. Q.V. DINH, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, Solving Elliptic Problems by Domain
Decomposition Methods with Applications, in Elliptic Problem Solvers II,
G. Birkhoff, A. Schoenstadt, eds., Academic Press, Orlando, 1984, pp.
395-426.
93. R. GLOWINSKI, B. MANTEL, J. PERIAUX, O. TISSIER, Finite element analysis
of laminar viscous flow over a step by nonlinear least squares and alternating
direction methods, in Analysis of Laminar Flow over a Backward Facing
Step, K. Morgan, J. Periaux, F. Thomasset, eds., Notes on Numerical Fluid
Mechanics, Vol. 9, Vieweg, Braunschweig/Wiesbaden, 1984.
94. M. O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, B. MANTEL, J. PERIAUX, P. PERRIER, Numerical
methods for the time dependent compressible Navier-Stokes equations, in
Computing Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering, VI, R. Glowinski
and J. L. Lions, eds., North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1984.
95. R. GLOWINSKI, P. LE TALLEC, Numerical solution of problems in
incompressible finite elasticity by augmented lagrangian methods (II).
Three-dimensional problems, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 44, (1984), 4,
pp. 710-733.
96. E. SCHATZMAN, A. MAEDER, F. ANGRAND, R. GLOWINSKI, Stellar Evolution with
Turbulent Diffusion Mixing. III: The Solar Model and the Neutrino Problem,
Astron. Astrophys., 96, (1981), pp. 1-16.
97. R. GLOWINSKI, P. LE TALLEC, Numerical solution of nonlinear boundary value
problems by quadratic minimization techniques, in Large scale scientific
computation, S. Parter ed., Academic Press, New York, 1984, pp. 23-49.
98. M. O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, B. MANTEL, J. PERIAUX, Finite Element
Methods for solving the Navier-Stokes Equations for Compressible Unsteady
Flows, in Ninth International Conference on Numerical Methods in Fluid
Dynamics, Soubbaramayer, J. P. Boujot eds., Lecture Notes in Physics,
Vol. 218, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1985, pp. 115-120.
99. M.O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, P. PERRIER, O. PIRONNEAU, G.
POIRIER, Finite Element Methods for Transonic Flow Calculations, in Advances
in Computational Transonics, Vol. 4, W. G. Habashi, Editor,
Pineridge Press, U. K., 1985, pp. 703-732.
100. R. GLOWINSKI, Numerical Solution of Nonlinear Boundary Value Problems by
Variational Methods. Applications, in Proceedings of the Int. Congress of
Mathematicians, August 16-24, 1983, Warsaw, North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1984,
pp. 1455-1508.
101. R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, Finite Element, Least Squares and Domain
Decomposition Methods for the Numerical Solution of Nonlinear Problems in Fluid
Dynamics, in Numerical Methods in Fluid Dynamics, Como 1983, F. Brezzi
ed., Lecture Notes in Mathematics, Vol. 1127, Springer-Verlag, Berlin,
1985, pp. 1-114.
102. R. GLOWINSKI, H. B. KELLER, L. REINHART, Continuation-conjugate gradient
methods for the least squares solution of nonlinear boundary value problems,
SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput., 4, (1985), 6, pp. 793-832.
103. M. BLANC, D. FONTAINE, R. GLOWINSKI, L. REINHART, Numerical simulations
of the magnetosospheric convection including the effects of electron
precipitation, Journal of Geophysical Research, Vol. 90, No. A9,
September 1, (1985), pp. 8343-8360.
104. M. O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, O. PIRONNEAU, G. POIRIER, On
the numerical solution of nonlinear problems in fluid dynamics by least squares
and finite element methods (II). Application to transonic flow simulations,
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 51,
(1985), pp. 363-394.
105. R. GLOWINSKI, P. LE TALLEC, Numerical Solution of Partial Differential
Equations Problems in Nonlinear Mechanics by Quadratic Minimization Methods, in
Colloque En l'Honneur de Laurent Schwartz, Vol. 2, Asterisque,
132, (1985), pp. 129-165.
106. R. GLOWINSKI, Viscous flow simulations by finite element methods and
related numerical techniques, in Progress in Supercomputing in Computational
Fluid Dynamics, E. M. Murman, S. S. Abarbanel eds., Birkhauser, Boston,
1985, pp. 173-210.
107. M. O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, B. MANTEL, J. PERIAUX, P. PERRIER,
Numerical Methods for Incompressible and Compressible Navier-Stokes Problems,
in Finite Elements in Fluids, Vol. 6, R. H. Gallagher, G. Carey,
J. T. Oden, O. C. Zienkiewicz, eds., J. Wiley, Chichester, 1985, pp. 1-40.
108. R. GLOWINSKI, Decomposition Methods in Scientific Computing: Application
to Fluid Calculations, in Innovative Numerical Methods in Engineering,
R. P. Shaw, J. Periaux, A. Chaudouet, J. Wu, C. Marino, C. A. Brebbia, eds.,
Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1986, pp. 1-15.
109. R. GLOWINSKI, P. LE TALLEC, M. VIDRASCU, Augmented Lagrangian Techniques
for Solving Frictionless Contact Problems in Finite Elasticity, in Finite
Element Methods for Nonlinear Problems, Europe-US Symposium, Bergan, Bathe,
Wunderlich eds., Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1986, pp. 745-758.
110. R. GLOWINSKI, Splitting methods for the numerical solution of the
incompressible Navier-Stokes equations, in Vistas in Applied
Mathematics, A. V. Balakrishnan, A. A. Dorodnitsyn, J. L. Lions, eds.,
Optimzation Software, New York, 1986, pp. 57-95.
111. M. O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, B. MANTEL, J. PERIAUX, C. POULETTY, G. S.
SINGH, Implicit and semi-implicit methods for the compressible Navier-Stokes
equations, in Proceedings of the Sixth GAMM-Conference on Numerical Methods
in Fluid Dynamics, D. Rues, W. Kordulla, eds., Vieweg and Sohn,
Braunschweig/Wiesbaden, 1986, pp. 9-22.
112. Q. V. DINH, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, G. TERRASSON, On the coupling of
incompressible viscous flows and incompressible potential flows via domain
decomposition, in Tenth International Conference on Numerical Methods in
Fluids Dynamics, Proceedings, Beijing, 1986, F. G. Zhaung, Y. L. Zhu, eds.
Lecture Notes in Physics, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1986, pp. 229-234.
113. R. GLOWINSKI, Finite Elements Methods for Variational Inequalities,
Chapter 7 of Part 1 of Finite Element Handbook, H. Kardestuncer, D. H.
Norrie eds., McGraw-Hill, New York, 1987, pp. 3.229-3.243.
114. M.O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, P. PERRIER, O. PIRONNEAU, G.
POIRIER, Transonic Flow and Shock Waves: Least-squares and Conjugate Gradient
Methods, Section 4.3 of Part 3 of Finite Element Handbook, H.
Kardestuncer, D. H. Norrie eds., McGraw-Hill, New York, 1987, pp. 3.229 -
3.243.
115. G. AUCHMUTY, E. J. DEAN, R. GLOWINSKI, S. C. ZHANG, Control Methods for
the Numerical Computation of Periodic Solutions of Autonomous Differential
Equations, in Control Problems for Systems Described by Partial Differential
Equations and Applications, I. Lasiecka, R. Triggiani eds., Lecture Notes
in Control and Information Sciences, Vol. 97, Springer-Verlag, Berlin,
1987, pp. 64-89.
116. M.O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, Numerical Methods for the
Navier-Stokes Equations. Applications to the simulation of compressible and
incompressible viscous flow, Computer Physics Reports, 6, (1987),
pp. 73-187.
117. M.O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, H. VIVIAND, Presentation of
Problems and Discussion from Results, in Numerical Simulation of
Compressible Navier-Stokes Flows, M. O. Bristeau, R. Glowinski, J. Periaux,
H. Viviand eds., Vieweg, Braunschweig/Wiesbaden, 1987, pp. 1-40.
118. M. O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, B. MANTEL, J. PERIAUX, C. POULETTY,
Solution of the Compressible Navier-Stokes Equations by least-squares and
finite element methods, in Numerical Simulation of Compressible
Navier-Stokes Flows, M. O. Bristeau, R. Glowinski, J. Periaux, H. Viviand
eds., Vieweg, Braunschweig/Wiesbaden, 1987, pp. 85-104.
119. T. E. TEZDUYAR, R. GLOWINSKI, F. GLAISNER,
Streamlines-upwind/Petrov-Galerkin procedures for the vorticity-stream function
form of the Navier-Stokes equations, in Numerical Methods in Laminar and
Turbulent Flow, Vol. 5, Part 1, C. Taylor, W. G. Habashi, M. M.
Hafez, eds., Pineridge Press, Swansea, 1987, pp. 197-209.
120. C. BEGUE, Q. V. DINH, B. MANTEL, J. PERIAUX, G. TERRASSON, B. CARDOT, F.
EL DABAGHI, F. HECHT, R. MUNOZ, C. PAREZ, O. PIRONNEAU, M. ABDALAS, R.
GLOWINSKI, Current progress on the numerical simulation of detached flows
around airplanes, in Numerical Methods in Laminar and Turbulent Flow,
Vol. 5, Part 2, C. Taylor, W. G. Habashi, M. M. Hafez, eds.,1987, pp.
1887-1921.
121. R. GLOWINSKI, On a new preconditioner for the Stokes Problem, Math.
Applic. Comp., 6, (1987), 2, pp. 123-140.
122. E. DEAN, R. GLOWINSKI, C. H. LI, Applications of Operator Splitting
Methods to the Numerical Solution of Nonlinear Problems in Continuum Mechanics
and Physics, in Mathematics Applied to Science, J. Goldstein, S.
Rosencrans, G. Sod, eds., Academic Press, Boston, 1988, pp. 13-64.
123. R. GLOWINSKI, Multigrid Methods, in Systems and Control
Encyclopedia, M. G. Singh ed., Pergammon, Oxford, 1988, pp. 3135-3140.
124. R. GLOWINSKI, M. F. WHEELER, Domain Decomposition and Mixed Finite
Element Methods for Elliptic Problems, in Domain Decomposition Methods for
Partial Differential Equations, R. Glowinski, G. H. Golub, G. Meurant, J.
Periaux eds., SIAM, Philadelphia, 1988, pp. 144-172.
125. Q. V. DINH, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, G. TERRASSON, On the Coupling of
Viscous and Inviscid Models for Incompressible Fluid Flows via Domain
Decomposition, in Domain Decomposition Methods for Partial Differential
Equations, R. Glowinski, G. H. Golub, G. Meurant, J. Periaux eds., SIAM,
Philadelphia, 1988, pp. 350-369.
126. R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, Numerical Methods for Nonlinear Problems in
Fluid Dynamics, in Supercomputing, A. Lichnewsky, C. Saguez eds., North
Holland, Amsterdam, 1987, pp. 381-479.
127. E. J. DEAN, R. GLOWINSKI, C.H. LI, Numerical solution of parabolic
problems in high dimensions, in ARO Report 88-1, Transactions of the Fifth
Army Conference on Applied Mathematics and Computing, 1988, pp. 207-285.
128. R. GLOWINSKI, Spectral Methods, in Systems and Control
Encyclopedia, M. G. Singh ed., Pergamon, Oxford, 1988, pp. 4495-4498.
129. C. BEGUE , M.O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, B. MANTEL, J. PERIAUX,
Acceleration of the convergence for viscous flow calculations, in Numeta
87, Vol. 2, C. N. Pande, J. Middleton eds., Martinus Nighoff
Publishers, Dordrecht, 1987, pp. T4/1 - T4/20.
130. C. BEGUE, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, Détermination d'un
opérateur de préconditionnement pour la résolution
itérative du problème de Stokes dans la formulation
d'Helmholtz, C. R. Acad. Sc., Paris, T. 306. S I, (1988), pp.
247-252.
131. T. E. TEZDUYAR, J. LIOU, R. GLOWINSKI, T. NGUYEN, S. POOLE, Block
iterative finite element computation for incompressible flow problems, in
Proceedings of the 1988 International Conference on Supercomputing, ACM,
New York, 1988, pp. 284-294.
132. M. O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, B. MANTEL, J. PERIAUX, G. S. SINGH, On the
use of subcycling for solving the compressible Navier-Stokes equations by
operator splitting and finite element methods, Comm. Appl. Num.
Meth., 4, (1988), pp. 309-317.
133. J. F. BOURGAT, R. GLOWINSKI, P. LE TALLEC, Formulation variationnelle et
algorithme de décomposition de domaines pour les problèmes
elliptiques, C. R. Acad. Sc., Paris, T. 306, S. I,(1988), pp.
569-572.
134. R. GLOWINSKI, J. LIOU, T. E. TEZDUYAR, Petrov-Galerkin methods on
multiply connected domains for the vorticity-stream function formulation of the
incompressible Navier-Stokes equations, Int. J. Num. Meth Fluids,
8, (1988), pp. 1269-1290.
135. J. F. BOURGAT, R. GLOWINSKI, P. LE TALLEC, M. VIDRASCU, Variational
formulation and algorithm for trace operator in domain decomposition
calculations, Chapter 1 of Domain Decomposition Methods, T. F. Chan, R.
GLOWINSKI, J. Periaux, O. Widlund, eds, SIAM, Philadelphia, 1989, pp. 3-16.
136. M. O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, Acceleration procedures for the
numerical simulation of compressible and incompressible viscous flows, Chapter
6 of Advances in Computational Nonlinear Mechanics, I.S. Doltsinis ed.,
Springer, Wien, 1989, pp. 197-243.
137. R. J. ELLIOT, R. GLOWINSKI, Approximation to solutions of the Zakai
filtering equations, Stochastic Analysis and Applications, 7,
(1989), 2, pp. 145-168.
138. E. J. DEAN, R. GLOWINSKI, C. H. LI, Supercomputer solutions of partial
differential equation problems in Computational Fluid Dynamics and in Control,
Computer Physics Communications, 53, (1989), pp. 401-439.
139. R. GLOWINSKI, Supercomputing and the finite element approximation of the
Navier-Strokes equations for incompressible viscous fluids, in Recent
Advances in Computational Fluid Dynamics, C. C. Chao, S.A. Orszag, W. Shyy
eds., Lecture Notes in Engineering, Vol. 43, Springer-Verlag, Berlin,
1989, pp. 277-315.
140. R. GLOWINSKI, A multiplier/element by element method for a class of
nonlinear boundary value problems, Chapter 15 of Parallel Supercomputing:
Methods, Algorithms and Applications, G. F. Carey ed., Wiley, Chichester,
1989, pp. 239-254.
141. G. BALLAL, C. H. LI, R. GLOWINSKI, N. R. AMUNDSON, Single particle char
combustion and gasification, Computer Methods Appl. Mech. Eng.,
75, (1989), pp. 467-479.
142. R. GLOWINSKI, C. H. LI, J. L. LIONS, A numerical approach to the exact
boundary controllability of the wave equation (I) Dirichlet controls:
Description of the numerical methods, Japan J. Appl. Math., 7,
(1990), pp. 1-76.
143. R. GLOWINSKI, W. KINTON, M. F. WHEELER, A mixed finite element
formulation for the boundary controllability of the wave equation, Int. J.
Num. Meth. Eng., 27, (1989), pp. 623-635.
144. R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, G. TERRASSON, On the coupling of viscous and
inviscid models for compressible fluid flows via domain decomposition, in
Domain Decomposition Methods for Partial Differential Equations, T. F.
Chan, R. Glowinski, J. Periaux, O. Widlund eds., SIAM, Philadelphia, 1990, pp.
64-97.
145. R. GLOWINSKI, P. LE TALLEC, Augmented Lagrangian interpretation of the
nonoverlapping Schwarz alternating method, in Domain Decomposition Methods
for Partial Differential Equations, T. F. Chan, R. Glowinski, J. Periaux,
O. Widlund eds., SIAM, Philadelphia, 1990, pp. 224-231.
146. R. GLOWINSKI, W. KINTON, M. F. WHEELER, Acceleration of Domain
Decomposition Algorithms for Mixed Finite Elements by Multi-level Methods, in
Domain Decomposition Methods for Partial Differential Equations, T. F.
Chan, R. Glowinski, J. Periaux, O. Widlund eds., SIAM, Philadelphia, 1990, pp.
263-289.
147. M. O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, L. DUTTO, J. PERIAUX, G. ROGE, Compressible
viscous flow calculations using compatible finite element approximations,
Int. J. Num. Meth. in Fluids, 11, (1990), 6, pp. 719-749.
148. R. GLOWINSKI, C. H. LI, On the numerical implementation of the Hilbert
Uniqueness Method for the exact boundary controllability of the wave
equation, C. R. Adad. Sc., Paris, T. 311, Serie I, (1990), pp.
135-142.
149. E. J. DEAN, R. GLOWINSKI, Y. M. KUO, M. G. NASSER, On the discretization
of some second order in time differential equations. Applications to nonlinear
wave problems, in Computational Techniques in Identification and Control of
Flexible Flight Structures, A. V. Balakrishnan ed., Optimization Software,
Inc., Los Angeles, 1990, pp. 199-246.
150. A. BENSOUSSAN, R. GLOWINSKI, A. RASCANU, Approximation of the Zakai
equation by the splitting up method, SIAM J. Control and
Optimization, 28, (1990), 6, pp. 1420-1431.
151. R. GLOWINSKI, W. LAWTON, M. RAVACHOL, E. TENEBAUM, Wavelet solution of
linear and nonlinear elliptic, parabolic and hyperbolic problems in one space
dimension, in Computing Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering, R.
Glowinski and A. Lichnewsky eds., SIAM, Philadelphia, 1990, pp. 55-120.
152. F. BOURGAT, R. GLOWINSKI, P. LE TALLEC, J. F. PALMIER, The periodic
Boltzmann Semiconductor equation, in Computing Methods in Applied Sciences
and Engineering, R. Glowinski and A. Lichnewsky, eds., SIAM, Philadelphia,
1990, pp. 325-349.
153. R. GLOWINSKI, C. H. LI, On the Exact Neumann Boundary Control of Wave
Equations, in Mathematical and Numerical Aspects of Wave Propagation
Phenomena, G. Cohen, L. Halpern, P. Joly, eds., SIAM, Philadelphia, 1991,
pp. 15-24.
154. C. ATAMIAN, Q. V. DINH, R. GLOWINSKI, J. HE, J. PERIAUX, Control Approach
to Fictitious-Domain Methods. Application to Fluid Dynamics and
Electromagnetics, in Fourth International Symposium on Domain Decomposition
Methods for Partial Differential Equations, R. Glowinski, Y. A. Kuznetsov,
G. Meurant, J. Periaux, O. B. Widlund eds., SIAM, Philadelphia, 1991,pp.
275-309.
155. H. CARLSSON, R. GLOWINSKI, Vibrations of Euler-Bernouilli Beams with
Pointwise Obstacles, in Advances in Kinetic Theory and Continuum
Mechanics, R. Gatignol and Soubbaramayer eds., Springer-Verlag, Berlin,
1991, pp. 261-275.
156. E. J. DEAN, R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, Iterative solution of the stream
function-vorticity formulation of the Stokes problem. Application to the
numerical simulation of incompressible viscous flow, Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech.
Eng., 81, (1991), pp. 117-156.
157. R. GLOWINSKI, T. W. PAN, J. PERIAUX, M. RAVACHOL, A fictitious domain
method for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations, in The Finite Element
Method in the 1990's, E. Onate, J. Periaux, A. Samuelson eds.,
Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1991, pp. 440-457.
158. C. ATAMIAN, Q. V. DINH, R. GLOWINSKI, J. W. HE, J. PERIAUX, On some
imbedding methods applied to fluid dynamics and electro-magnetics, Comp.
Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng., 91, (1991), pp. 1271-1299.
159. R. GLOWINSKI, Finite element methods for the numerical simulation of
incompressible viscous flow. Introduction to the control of the Navier-Stokes
equations, in Vortex Dynamics and Vortex Methods, C. R. Anderson and C.
Greengard eds., Lectures in Applied Mathematics, Vol. 28, AMS,
Providence, R. I., 1991, pp. 219-301.
160. R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, Finite Element Methods for Navier-Stokes
Equations, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech., 24, (1992), pp. 167-204.
161. A. BENSOUSSAN, R. GLOWINSKI, A. RASCANU, Approximation of Some Stochastic
Differential Equations by the Splitting Up Method, Appl. Math. Opt.,
25, (1992), pp. 81-106.
162. E. J. DEAN, R. GLOWINSKI, Y. M. KUO, G. NASSER, Multiplier techniques for
some dynamical systems with dry friction, C. R. Acad. Sc., Paris, T.
314, Serie I, (1992), pp. 153-159.
163. T. DUPONT, R. GLOWINSKI, W. KINTON, M. F. WHEELER, Mixed finite-element
methods for time-dependent problems: application to control, in Finite
Element in Fluids, Vol. 8, T. J. Chung ed., Hemisphere Publishing
Corporation, Washington, D.C., 1992, pp. 119-136.
164. R. GLOWINSKI, P. LE TALLEC, M. RAVACHOL, V. TSIKKINIS, Numerical Solution
of the Navier-Stokes equations modelling the flow of incompressible nonmiscible
viscous fluids, in Finite Element in Fluids, Vol. 8, T. J. Chung
ed., Hemisphere Publishing Corporation, Washington, D.C., 1992, pp. 137-163.
165. T. E. TEZDUYAR, J. LIOU, D. K. GANJOO, M. BEHR, R. GLOWINSKI, Unsteady
incompressible flow computations with the finite-element method, in Finite
Element in Fluids, Vol. 8, T. J. Chung ed., Hemisphere Publishing
Corporation, Washington, D.C., 1992, pp. 177-209.
166. R. GLOWINSKI, Boundary controllability problems for the wave and heat
equations, in Boundary Control and Boundary Variation, J. P. Zolesio ed.,
Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences, Vol. 178,
Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1992, pp. 221-237.
167. Y. ACHDOU, R. GLOWINSKI, O. PIRONNEAU, Tuning the mesh of a mixed method
for the stream function-vorticity formulation of the Navier-Stokes equations,
Num. Math., 63, (1992), 2, pp. 145-163.
168. L. C. COWSAR, E. J. DEAN, R. GLOWINSKI, P. LE TALLEC, C. H. LI, J.
PERIAUX, M. F. WHEELER, Decomposition principles and their applications in
scientific computing, in Parallel Processing for Scientific Computing,
J. Dongarra, K. Kennedy, P. Messina, D. C. Sorensen, R. G. Voigt eds., SIAM,
Philadelphia, 1992, pp. 213-237.
169. Q. V. DINH, R. GLOWINSKI, J. HE, V. KWOCK, T. W. PAN, J. PERIAUX,
Lagrange multiplier approach to fictitious domain methods: application to fluid
dynamics and electro-magnetics, in Domain Decomposition Methods for Partial
Differential Equations, D. E. Keyes, T. F. Chan, G. Meurant, J. S. Scroggs,
R. G. Voigt eds., SIAM, Philadelphia, 1992, pp. 151-194.
170. E. J. DEAN, Q. V. DINH, R. GLOWINSKI, J. HE, T. W. PAN, J. PERIAUX, Least
squares/domain imbedding methods for Neumann problems: application to fluid
dynamics, in Domain Decomposition Methods for Partial Differential
Equations, D. E. Keyes, T. F. Chan, G. Meurant, J. S. Scroggs, R. G. Voigt
eds., SIAM, Philadelphia, 1992, pp. 451-475.
171. R. GLOWINSKI, Ensuring Well-Posedness by Analogy; Stokes Problem and
Boundary Control for the Wave Equation, J. Comput. Phys., 103,
(1992), 2, pp. 189-221.
172. R. GLOWINSKI, T. W. PAN, Error estimates for fictitious
domain/penalty/finite element methods, Calcolo, 29, (1992), 12,
pp. 125-141.
173. M. O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, L. DUTTO, G. ROGE, On recent numerical
simulations of compressible Navier-Stokes flows, in Numerical Simulation of
Unsteady Flows and Transition to Turbulence, O. Pironneau, W. Rodi, I. L.
Ryhming, A. H. Savill, T. V. Truong eds., Cambridge University Press, 1992, pp.
444-472.
174. R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, M. RAVACHOL, T. W. PAN, R. O. WELLS, X. ZHOU,
Wavelet methods in Computational Fluid Dynamics, in Algorithmic Trends in
Computational Fluid Dynamics, M. Y. Hussainy, A. Kumar, M. D. Salas eds.,
Springer-Verlag, New York, N. Y., 1993, pp. 259-276.
175. M. O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, Using exact controllability to
solve the Helmholtz equation at high wave numbers, Chapter 12 of
Mathematical and Numerical Aspects of Wave Propagation, R. Kleinman, Th.
Angell, D. Colton, F. Santosa, I. Strakgold eds., SIAM, Philadelphia,
Pennsylvania, 1993, pp. 113-127.
176. E. J. DEAN, R. GLOWINSKI, On some finite element methods for the
numerical simulation of incompressible viscous flow, in Incompressible
Computational Fluid Dynamics, M.D. Gunzburger, R.A. Nicolaides eds.,
Cambridge University Press, New York, N. Y., 1993, pp. 109-150.
177. R. GLOWINSKI, T. W. PAN, J. PERIAUX, Fictitious domain methods for the
Dirichlet problem and its generalization to some flow problems, in Finite
Elements in Fluids, New Trends and Applications, Part I, K. Morgan, E.
Onate, J. Periaux, J. Peraire, O. C. Zienkiewicz eds., Pineridge Press,
Barcelona, 1993, pp. 347-368.
178. R. GLOWINSKI, T. W. PAN, A least squares/fictitious domain method for
mixed problems and Neumann problems, in Boundary Value Problems for Partial
Differential Equations and Applications, J. L. Lions and C. Baiocchi eds.,
Masson, Paris, 1993.
179. R. GLOWINSKI, Q. H. TRAN, Constrained optimization in reflection
tomography: the augmented Lagrangian method, East-West J. Num. Math.,
1, (1993), 3, pp. 213-234.
180. M. O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, Scattering wave simulation
using exact controllability methods, 31st Aerospace Sciences Meeting,
Reno, Nevada, AIAA Paper 930460, 1993.
181. M. O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, Numerical simulation of
high-frequency scattering waves using exact controllability methods, in
Nonlinear Hyperbolic Problems: Theoretical Applied, and Computation
Aspects, A. Donato, F. Oliveri eds., Notes in Numerical Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 43, Vieweg, Branschweig, 1993, pp. 86-108.
182. M. O BRISTEAU, J. ERHEL, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, A time dependent
approach to the solution of the Helmholtz equation at high wave numbers, in
Proceedings of the Sixth SIAM Conference on Parallel Processing for
Scientific Computing, R. F. Sincorce, D. Keyes, M. R. Lenzo, L. Petzold, D.
A. Reed eds., SIAM, Philadelphia, Penn., 1993.
183. E. DEAN, R. GLOWINSKI, A domain decomposition method for the wave
equation, Les Grands Systèmes des Sciences et de la Technologie,
J. Horowitz, J. L. Lions eds., Masson, Paris, 1993, pp. 241-264.
184. R. GLOWINSKI, T. W. PAN, J. PERIAUX, A one shot domain
decomposition/fictitious domain methods for the Stokes problem, in Advances
in Finite Element Analysis in Fluid Dynamics-1993, M. N. Dhaubhadel, M. S.
Engelman, W. G. Habashi eds., ASME, Fairfield, N. J., 1993, pp. 115-124.
185. M. SUN, R. GLOWINSKI, Pathwise approximation and simulation for the Zakai
filtering equation through operator splitting, Calcolo, 30, (1993), 3,
pp.219-239.
186. R. GLOWINSKI, T. W. PAN, J. PERIAUX, A fictitious domain method for
unsteady incompressible viscous flow modeled by Navier-Stokes equations, in
Domain Decomposition Methods in Science and Engineering, A. Quarteroni,
J. Periaux, Y. A. Kuznetsov, O. B. Widlund eds., AMS, Providence, R.I., 1994,
pp. 421-431.
187. R. GLOWINSKI, T. W. PAN, J. PERIAUX, A fictitious domain method for
Dirichlet problem and applications, Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng.,
111, (1994), pp. 283-303.
188. R. GLOWINSKI, T. W. PAN, J. PERIAUX, A fictitious domain method for
external incompressible viscous flow modeled by Navier-Stokes equations,
Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng., 112, (1994), pp. 133-148.
189. M. O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, On the numerical solution of
the Helmholtz equation at large wave numbers using exact controllability
methods. Application to scattering, in Domain Decomposition Methods in
Science and Engineering, A. Quarteroni, J. Periaux, Y. A. Kuznetsov, O. B.
Widlund eds., AMS, Providence, R.I., 1994, pp. 399-419.
190. R. GLOWINSKI, J. L. LIONS, Exact and approximate controllability for
distributed parameter systems (I), Acta Numerica, (1994), pp. 269-378.
191. C. CARTHEL, R. GLOWINSKI, J. L. LIONS, On Exact and Approximate Boundary
Controllabilities for the Heat Equation: A Numerical Approach, J. Optim. Th.
and Appl., 82, (1994), 3, pp. 429-484.
192. F. S. ZHANG, F. SPIEGELMANN, E. SURAUD, V. FRAYSSE, R. POTEAU, R.
GLOWINSKI, F. CHATELIN, On the formation of transient (Na19)2 and (Na20)2
cluster dimers from molecular dynamics simulation, Physics Letters A,
193, (1994), pp.75-81.
193. H. Q. CHEN, R. GLOWINSKI, J. W. HE, A. J. KEARSLEY, J. PERIAUX, O.
PIRONNEAU, Remarks on optimal shape design problems, in Frontiers of
Computational Fluid Dynamics, 1994, D. A. Caughey and M. M. Hafez, eds.,
Wiley, Chichester, 1994, pp. 67-80.
194. M. O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, On the numerical solution of
the Helmholtz equation at large wave numbers using exact controllability
methods. Application to scattering, in Contemporary Mathematics, Vol.
157, AMS, Providence, R.I., 1994, pp. 399-419.
195. R. GLOWINSKI, T. W. PAN, J. PERIAUX, A One Shot Domain Decomposition /
Fictitious Domain Method for the Navier-Stokes Equations, in Contemporary
Mathematics, Vol. 180, AMS, Providence, R.I., 1994, pp. 211-222.
196. M.O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, Exact Controllability to solve
the Helmholtz Equation with Absorbing Boundary Conditions, in Finite Element
Methods: Fifty Years of the Courant Elements, K. Krizek, P. Neittaanmaki,
R. Stenberg, eds., Marcel Dekker, New York, N.Y., 1994, p. 75-93.
197. J. FENG, D. D. JOSEPH, R. GLOWINSKI, T. W. PAN, A three-dimensional
computation of the force and torque on an ellipsoid settling slowly through a
viscoelastic fluid, J. Fluid Mech., Vol. 283, (1995), Cambridge,
pp.1-16.
198. R. GLOWINSKI, T. W. PAN, J. PERIAUX, A Lagrange Multiplier / Fictitious
Domain Method for the Dirichlet Problem - Generalization to Some Flow Problems,
Japan J. of Ind. and Appl. Math., Vol. 12, (1995), 1, pp.
87-108.
199. R. GLOWINSKI, T. W. PAN, J. PERIAUX, A One Shot Domain Decomposition /
Fictitious Domain Method for the Solution of Elliptic Equations, in Parallel
Computational Fluid Dynamics: New Trends and Advances, A. Ecer, J. Hausen,
P. Leca, J. Periaux, eds., North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1995, pp. 317-324.
200. R. GLOWINSKI, T. W. PAN, J. PERIAUX, Fictitious Domain / Domain
Decomposition Methods for Partial Differential Equations, Chapter 11 of
Domain-Based Parallelism and Problem Decomposition Methods in Computational
Science and Engineering, D. E. Keyes, Y. Saad, D. G. Truhlar, eds., SIAM,
Philadelphia, 1995, pp. 177-192.
201. R. GLOWINSKI, T. W. PAN, A. J. KEARSLEY, J. PERIAUX, Numerical Simulation
and Optimal Shape for Viscous Flow by a Fictitious Domain Method, Int. J.
Num. Meth. Fluids, Vol. 20, (1995), pp. 695-711.
202. R. GLOWINSKI, J. L. LIONS, Exact and approximate controllability for
distributed parameter systems (II), Acta Numerica, (1995), pp.
159-333.
203. M. BERGGREN, R. GLOWINSKI, A spectral preconditioner for control problems
associated with linear evolution equations, East-West Journal of Numerical
Mathematics, Vol. 3, (1995), 2, pp. 81-110.
204. R. GLOWINSKI, A. J. KEARSLEY, On the simulation and control of some
friction constrained motions, SIAM J. of Optimization, Vol.
5,(1995), 3, pp. 681-694.
205. R. GLOWINSKI, M. HOLMSTROM, Constrained motion problems with applications
by nonlinear programming methods, Surveys on Math. for Industry,
5, (1995), pp. 75-108.
206. M. O. BRISTEAU, E. J. DEAN, R. GLOWINSKI, V. KWOK, J. PERIAUX,
Application of exact controllability to the computation of scattering waves,
Control Problems in Industry, I. Lasiecka and B. Morton, eds., Birkhauser,
Boston, (1995), pp.17-41.
207. V. GIRAULT, R. GLOWINSKI, Error analysis of a fictitious domain method
applied to a Dirichlet problem, Japan Journal of Industrial and Applied
Mathematics, Vol. 12, (1995), pp. 487-514.
208. R. GLOWINSKI, A. J. KEARSLEY, T. W. PAN, J. PERIAUX, Fictitious domain
method for viscous flow simulation, Computational Fluid Dynamics Review
1995, M. Hafez, K. Oshima, eds., J. Wiley, Chichester, (1995),
pp.357-381.
209. M. O. BRISTEAU, J. ERHEL, P. FEAT, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, Solving the
Helmholtz equation at high-wave numbers on a parallel computer with a shared
virtual memory, International J. of Supercomputing Applications,
9, (1995), 1, pp.18-28.
210. R. GLOWINSKI, T. W. PAN, J. PERIAUX, One shot fictitious domain/domain
decomposition methods for three-dimensional elliptic problems. Parallel
implementation on a KSR1 machine, in Parallel Computational Fluid Dynamics:
New Algorithms and Applications, N. Satofuka, J. Periaux, A. Ecer, eds.,
Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, 1995, pp. 313-320.
211. C.H. LI, R. GLOWINSKI, Modelling and Numerical Simulation of
Low-Mach-number Compressible Flows, Int. J. Num. Meth. Fluids,
23, (1996), 2, pp. 77-103.
212. R. GLOWINSKI, T.W. PAN, R.O. WELLS, X. ZHOU, Wavelet and Finite Element
Solutions for the Neumann Problem Using Fictitious Domains, J. Comp.
Physics, 126, (1996), 1, pp. 40-51.
213. R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, M. SEFRIOUI, B. MANTEL, M.O. BRISTEAU, Optimal
Backscattering of an Active Reflector by means of Genetic Algorithms, in
Computational Methods in Applied Sciences, 96, J.A. Desideri, C.
Hirsh, P. LeTallec, E. Onate, M. Pandolfi, J. Periaux, E. Stein, eds., J.
Wiley, Chichester, 1996, pp. 251-257.
214. R. GLOWINSKI, T.W. PAN, J. PERIAUX, Fictitious Domain Methods for the
Simulation of Stokes Flow Past a Moving Disk, in Computational Fluid
Dynamics '96, in J.A. Desideri, C. Hirsh, P. LeTallec, M. Pandolfi,
J. Periaux, eds, J. Wiley, Chichester, 1996, pp. 64-70.
215. M.O. BRISTEAU, R. GLOWINSKI, J. PERIAUX, Wave Scattering Using Exact
Controllability, in Numerical Methods in Engineering '96, J.A. Desideri,
P. Le Tallec, E. Onate, J. Periaux, E. Stein, eds., J. Wiley, Chichester, 1996,
pp. 97-103.
216. E.J. DEAN, R. GLOWINSKI, D. TREVAS, An Approximate Factorization/Least
Squares Solution Method for a Mixed Finite Element Approximation of the
Cahn-Hilliard Equation, Japan Journal of Industrial and Applied
Mathematics, 13, (1996), 3, pp. 495-517.
217. R. GLOWINSKI, A. RIEDER, R.O. WELLS, X. ZHOU, A WaveletMultigrid
Preconditioner for Dirichlet Boundary Value Problems in General Domains,
Math. Modelling and Num. Anal. (M2AN), 30,
(1996), 6, pp. 711-729.
Roland Glowinski's biography
Homepage of the conference CS21
INRIA Ucis
 . u = 0.
This finding goes back to the late 1960's and it
led to a family of algorithms called Uzawa algorithms (since they are
related to algorithms for the search of economic equilibria investigated
by H. Uzawa). These algorithms, as applied to the solution of the
Stokes and Navier-Stokes equations, are described and analyzed in
references [B.4], [59], [82], [85], [101], [106], [110], [116],
[139], [159], [160], [171], [176]. Uzawa algorithms have motivated
the investigations of many authors and, although they were introduced
more than twenty-five years ago, they still provide efficient methods
for dealing with incompressibility and they continue to be widely used
by the scientific community.
. u = 0.
This finding goes back to the late 1960's and it
led to a family of algorithms called Uzawa algorithms (since they are
related to algorithms for the search of economic equilibria investigated
by H. Uzawa). These algorithms, as applied to the solution of the
Stokes and Navier-Stokes equations, are described and analyzed in
references [B.4], [59], [82], [85], [101], [106], [110], [116],
[139], [159], [160], [171], [176]. Uzawa algorithms have motivated
the investigations of many authors and, although they were introduced
more than twenty-five years ago, they still provide efficient methods
for dealing with incompressibility and they continue to be widely used
by the scientific community.
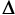 2 et méthode itérative de résolution du
problème approché (I), C. R. Acad. Sc., Paris, T. 275
A, (1972), pp. 201-204.
2 et méthode itérative de résolution du
problème approché (I), C. R. Acad. Sc., Paris, T. 275
A, (1972), pp. 201-204.